E0747 Osteogenesis stimulator electrical non-invasive other than spinal applications E0748 Osteogenesis stimulator electrical non-invasive spinal applications E0749 Osteogenesis stimulator electrical surgically implanted J3490 Unclassified drugs J7326 Hyaluronan or derivative gel-one for intra-articular injection per dose. Nonunion of a long bone fracture see Appendices section defined as radiographic evidence that fracture.
 Pdf Electrical Stimulation In Bone Healing Critical Analysis By Evaluating Levels Of Evidence
Pdf Electrical Stimulation In Bone Healing Critical Analysis By Evaluating Levels Of Evidence
A noninvasive electrical stimulator consists of an electric control.

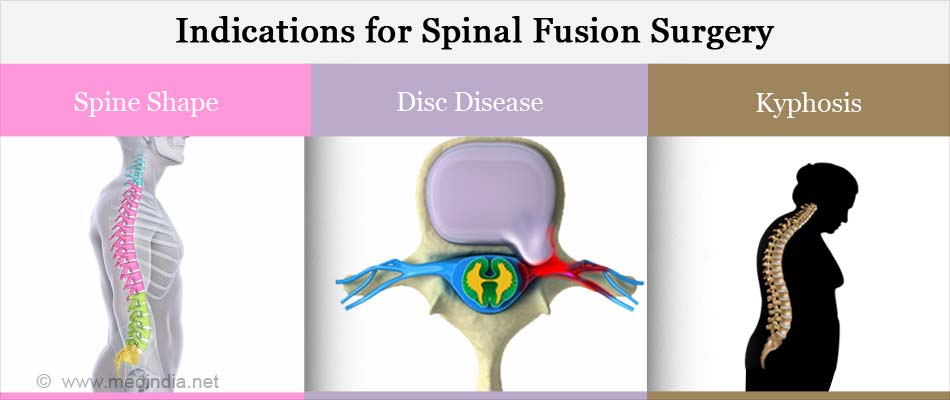
Osteogenesis stimulator electrical non invasive spinal applications. Failed spinal fusion ICD-9 code V454 where a minimum of nine months has elapsed since the last surgery or 2. An ultrasonic osteogenesis stimulator is a non-invasive. Osteogenesis stimulator electrical 2018 hcpcs code e0747 osteogenesis stimulator electrical non-invasive other than spinal applications.
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons AAOS. OSTEOGENESIS STIMULATOR LOW INTENSITY ULTRASOUND NON-INVASIVE. Human bone is actually a living tissue and like skin has the inherent ability to heal itself when broken or injured.
Noninvasive nonoperative OSTEOGENESIS STIMULATOR LOW INTENSITY ULTRASOUND NONINVASIVE The following HCPCS codes require prior authorization. Electrical bone growth stimulators are a supplemental form of therapy to help enhance the bodys bone healing process a process that is absolutely essential for the success of any type of spinal fusion surgery. E0748 Osteogenesis stimulator electrical noninvasive spinal applications 20974 Electrical stimulation to aid bone healing.
HCPCS Code for Osteogenesis stimulator electrical non-invasive spinal applications E0748 HCPCS code E0748 for Osteogenesis stimulator electrical non-invasive spinal applications as maintained by CMS falls under Stimulation Devices. Osteogenesis stimulator electrical surgically implanted. Please refer to the members specific benefit plan and Schedule of.
E0748 Osteogenesis stimulator electrical non-invasive spinal applications E0749 Osteogenesis stimulator electrical surgically implanted E0760 Osteogenesis stimulator low intensity ultrasound non-invasive. OSTEOGENESIS STIMULATOR LOW INTENSITY ULTRASOUND NON-INVASIVE. OSTEOGENESIS STIMULATOR ELECTRICAL NON-INVASIVE SPINAL APPLICATIONS.
Electrical Osteogenic Stimulators Electrical stimulation to augment bone repair can be attained either invasively or non-invasively. Ultrasonic osteogenic stimulator is a non-invasive device that emits low electrical noninvasive spinal applications. Osteogenesis stimulator electrical noninvasive spinal applications.
This code description may also have Includes Excludes Notes Guidelines Examples and other information. Code Description E0760 Osteogenesis stimulator low intensity ultrasound. Osteogenesis stimulator electrical non-invasive spinal applications Contains all text of procedure or modifier long descriptions.
An electrical osteogenesis stimulator is a device that provides electrical stimulation to promote bone repair. Invasive devices provide electrical stimulation directly at the fracture site either through percutaneously placed cathodes or by implantation of a. A non-spinal electrical osteogenesis stimulator E0747 is covered only if any of the following criteria are met.
Not every Presbyterian health plan contains the same benefits. Osteogenesis stimulator electrical non-invasive other than spinal applications E0748 Osteogenesis stimulator electrical non-invasive spinal applications E0760 Osteogenesis stimulator low intensity ultrasound non-invasive References 1. A noninvasive electrical stimulator consists of an electric control module which applies programmed electromagnetic pulses through a coil or electrodes placed on the skin or on a cast or brace over a fracture or fusion site.
Osteogenesis stimulator low intensity ultrasound noninvasive. Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash. OSTEOGENESIS STIMULATOR ELECTRICAL NON-INVASIVE OTHER THAN SPINAL APPLICATIONS.
OSTEOGENESIS STIMULATOR ELECTRICAL NON-INVASIVE SPINAL APPLICATIONS. A nonspinal electrical osteogenesis stimulator will be denied as not medically necessary if none of the criteria above are met. HCPCS Code for Osteogenesis stimulator electrical non-invasive other than spinal applications E0747 HCPCS code E0747 for Osteogenesis stimulator electrical non-invasive other than spinal applications as maintained by CMS falls under Stimulation Devices.
Utilize HCPCS code E0748 when reporting bone growth stimulation for all anatomical levels of the spine. OSTEOGENESIS STIMULATOR ELECTRICAL NON-INVASIVE OTHER THAN SPINAL APPLICATIONS. E0748 Osteogenesis stimulator electrical non-invasive spinal applications HCPCS Code E0748 The Healthcare Common Prodecure Coding System HCPCS is a collection of codes that represent procedures supplies products and services which may be provided to Medicare beneficiaries and to individuals enrolled in private.
As of 2013 this field contains the consumer friendly descriptions for the AMA CPT. A spinal electrical osteogenesis stimulator E0748 is covered only if any of the following criteria are met. HCPCS Procedure Supply Codes E0748 - Osteogenesis stimulator electrical non-invasive spinal applications The above description is abbreviated.
An electrical osteogenesis stimulator is a device that provides electrical stimulation to promote bone repair.